The Triad of Learning
Theory, Practice, and Error
bizibee Business Simulations
The Triad of Learning
Learning is a multifaceted process that involves a dynamic interplay between theory, practice, and the inevitable companion, error. Each component contributes uniquely to the overall journey of acquiring knowledge and skills.Theory
- Foundation of Understanding
- Theory provides a structured framework for understanding concepts, principles, and the underlying logic of a subject. It forms the intellectual foundation upon which practical knowledge can be built.
- Conceptual Framework
- Theoretical knowledge offers a conceptual framework, allowing individuals to grasp the "why" and "how" behind phenomena. It provides a roadmap for practical application.
Practice
- Application of Knowledge
- Practice is the bridge between theory and real-world scenarios. It involves actively engaging with concepts in practical situations, transforming abstract knowledge into tangible skills.
- Skill Development
- Through practice, individuals refine and develop skills. Repetition, experimentation, and application enhance competency and contribute to a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Error
- Learning Opportunities
- Errors are not setbacks but valuable learning opportunities. Mistakes prompt reflection and analysis, fostering a deeper understanding of both theory and practice. They reveal the limits of knowledge and highlight areas for improvement.
- Iterative Improvement
- Learning from errors is an iterative process. Each mistake becomes a stepping stone toward refinement. The ability to adapt, correct, and grow from errors is integral to the learning journey.
The Symbiosis of Theory and Practice
- Holistic Understanding
- While theory lays the groundwork, practice provides a context for application. The symbiotic relationship between theory and practice ensures a more holistic understanding of a subject, enabling individuals to navigate complex situations.
- Real-World Relevance
- Theory gains relevance through practical application. Theoretical knowledge gains depth and meaning when individuals can connect it to real-world scenarios, making it more applicable and valuable.
Learning from Theory, Practice, and Error in Action
- Experiential Learning
- The most effective learning often occurs when theory and practice are seamlessly integrated. Experiential learning, as championed by educators like John Dewey, emphasizes the importance of hands-on experiences to solidify theoretical understanding.
- Innovation and Creativity
- The synergy between theory and practice fuels innovation. The iterative nature of learning from errors encourages creative problem-solving, pushing boundaries, and fostering innovation in various fields.
Conclusion
The triad of theory, practice, and error forms a symbiotic relationship in the learning process. Theory provides the intellectual foundation, practice transforms knowledge into skills, and errors offer invaluable learning opportunities. Embracing this dynamic interplay results in a more comprehensive and adaptable approach to learning, preparing individuals for the complexities of an ever-evolving world.
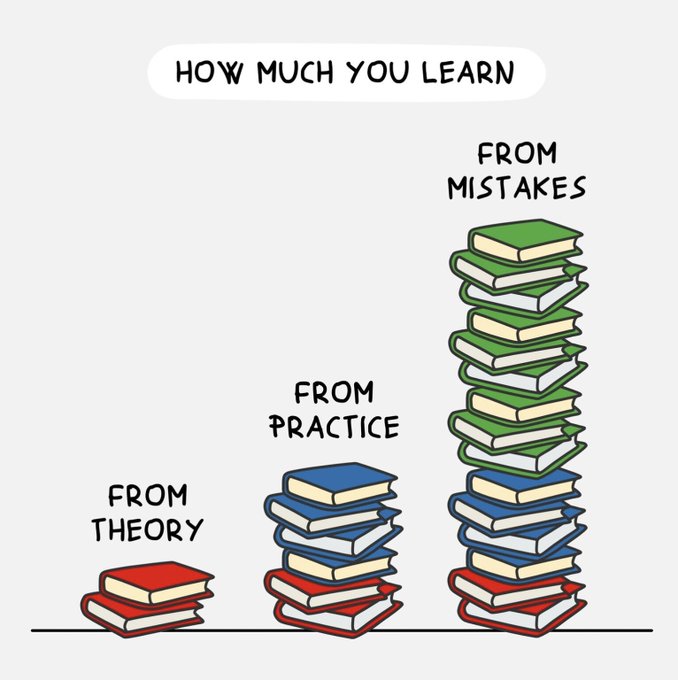
How much you learn
Thanks
bizibee Business Simulations
The hive of business knowledge
![]()